Sleep is one of the few moments in the day when we feel like we are doing nothing. We lie down, close our eyes, and slowly drift away from the noise of the world. From the outside, it looks peaceful and quiet. Inside the body, however, an extraordinary process begins.
The moment you fall asleep, your brain shifts into a highly organized state of activity. Systems that stay in the background all day suddenly take center stage. Memory gets sorted, emotions are processed, and hormones are released.
Sleep is the foundation that keeps the brain and body functioning in balance.
Understanding the science of sleep helps explain why quality sleep improves focus, mood, and resilience, and why disrupted sleep affects mental clarity, stress levels, and overall health far more than we often realize.
How the Brain Knows It Is Time to Sleep
Your brain doesn’t just guess when it’s bedtime. It runs on an internal clock called the circadian rhythm. Basically, there’s a tiny spot in your brain that keeps track of light and dark. As the sun goes down, your eyes send a message to your brain, and then melatonin kicks in. That’s the hormone that makes you feel sleepy. Your heart slows down a bit. You feel a little cooler. Muscles relax. None of these things is super dramatic, but together, they set the stage for sleep.
However, when something disrupts this rhythm, such as bright lights at night, scrolling through your phone in bed, staying up late, or simply being stressed, your brain receives mixed signals. Suddenly, your sleep isn’t as deep or refreshing, even if you’re technically in bed for enough hours.
The whole system just works better when you stick to a steady routine and let your brain know when it’s time to wind down.
Also read: How to fix your sleep schedule.
The Stages of Sleep and Their Purpose
Sleep isn’t just one thing happening all night. It actually moves through a series of stages, looping around a few times before morning comes.
Each stage does something different. Your body, brain, and mood all depend on this rhythm to really recharge for the next day. If you get to cycle through these stages naturally, you wake up feeling great. But when that flow gets thrown off, even a full night in bed leaves you dragging.
-
Stage One: Drifting Off
This is where you are barely asleep, just starting to let go.
Your brain slows down, your muscles go slack, and the world fades out.
You might twitch a little or have random thoughts. If something stirs you, you are up in a flash. Basically, this stage lets your mind ease out of alert mode and get ready for the real rest.
-
Stage Two: Settling In
Now sleep gets more solid. Your heart settles, you start breathing deeper, and you cool off a bit.
Your brain throws out quick bursts of activity, kind of like putting up a “do not disturb” sign. These bursts help you tune out noise and lock in memories. This stage bridges the gap between light sleep and the deep, heavy stuff.
-
Stage Three: Deep Sleep
This stage is often referred to as deep sleep. Brain waves slow significantly, and waking up during this phase can leave a person feeling groggy or disoriented. Deep sleep is when the body focuses on repair and regeneration.
Tissues heal, muscles recover, immune function strengthens, and growth-related hormones are released. This stage is essential for physical resilience, energy levels, and long-term health.
-
REM Sleep: Dream Time
After deep sleep, your brain switches gears into REM, short for rapid eye movement.
You dream most vividly here. Your brain lights up, but your body stays still (so you don’t act out your dreams). REM helps you handle emotions, get creative, and sort out memories. It’s your brain’s version of a tune-up, connecting ideas and dealing with the day’s stress.
Why Quality Matters More Than Hours
People love to track how many hours they sleep, but honestly, that’s only half the story. What really matters is whether those hours actually help your brain and body recharge.
Think about it: you can be in bed for eight hours, but if you’re tossing and turning, waking up a bunch of times, or stuck in light sleep, you’ll still wake up tired, cranky, and struggling to focus. That’s not real rest.
Good sleep feels different. Your body cycles smoothly through deeper stages, you spend enough time in REM, and your nervous system finally gets to relax. That’s why it’s not just about when you go to bed. Managing stress, keeping your routine steady, and letting your body wind down matter the most.
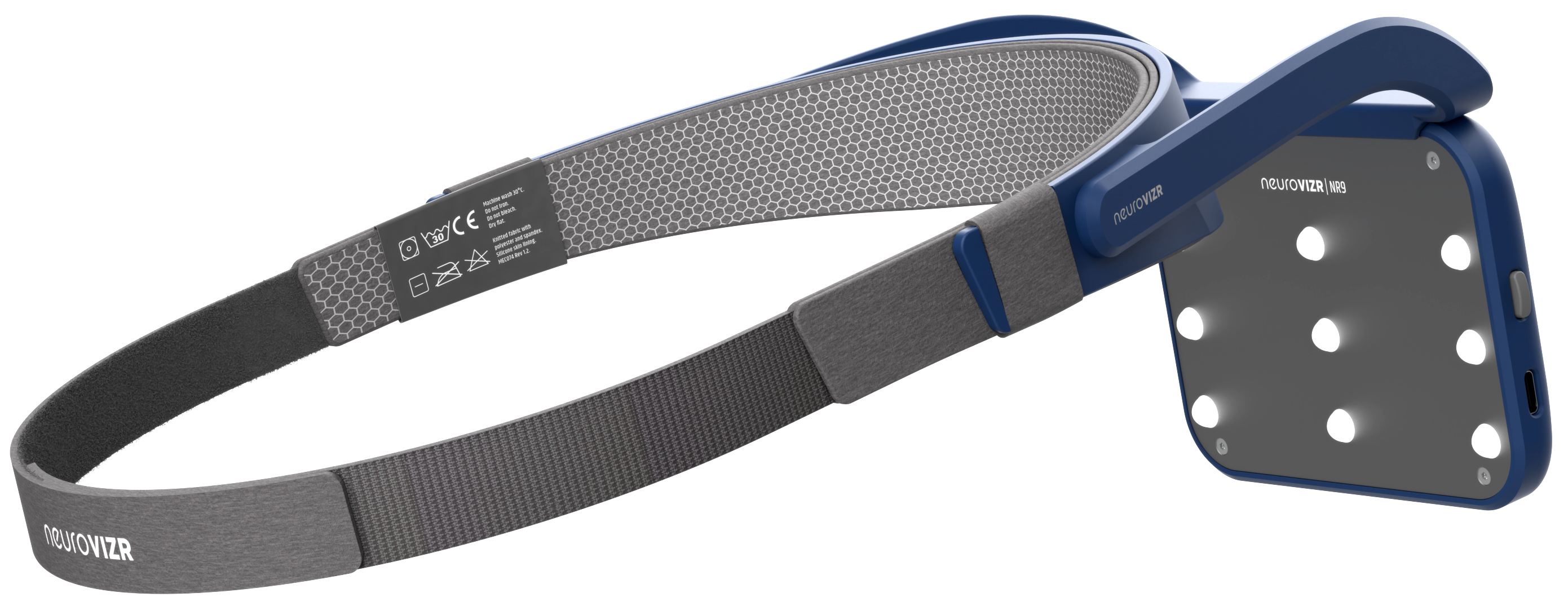
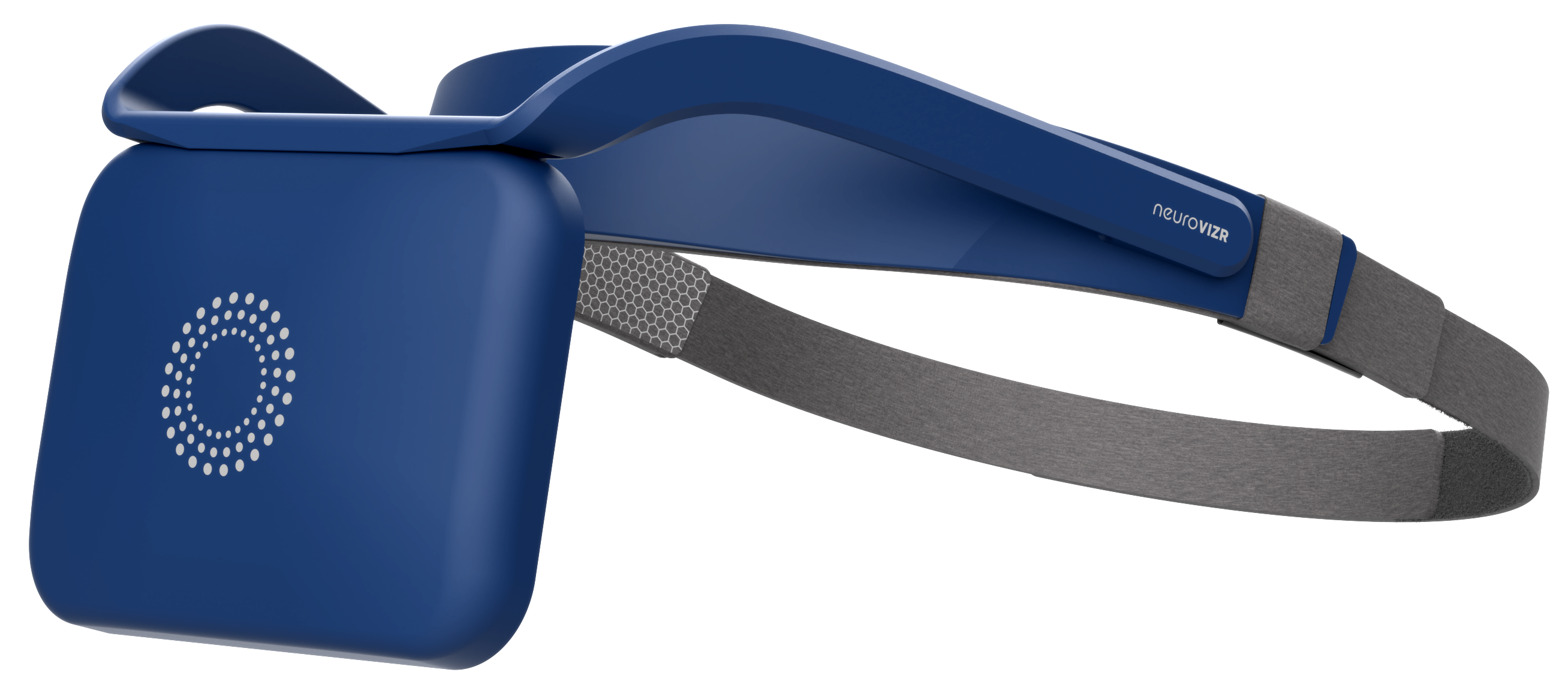
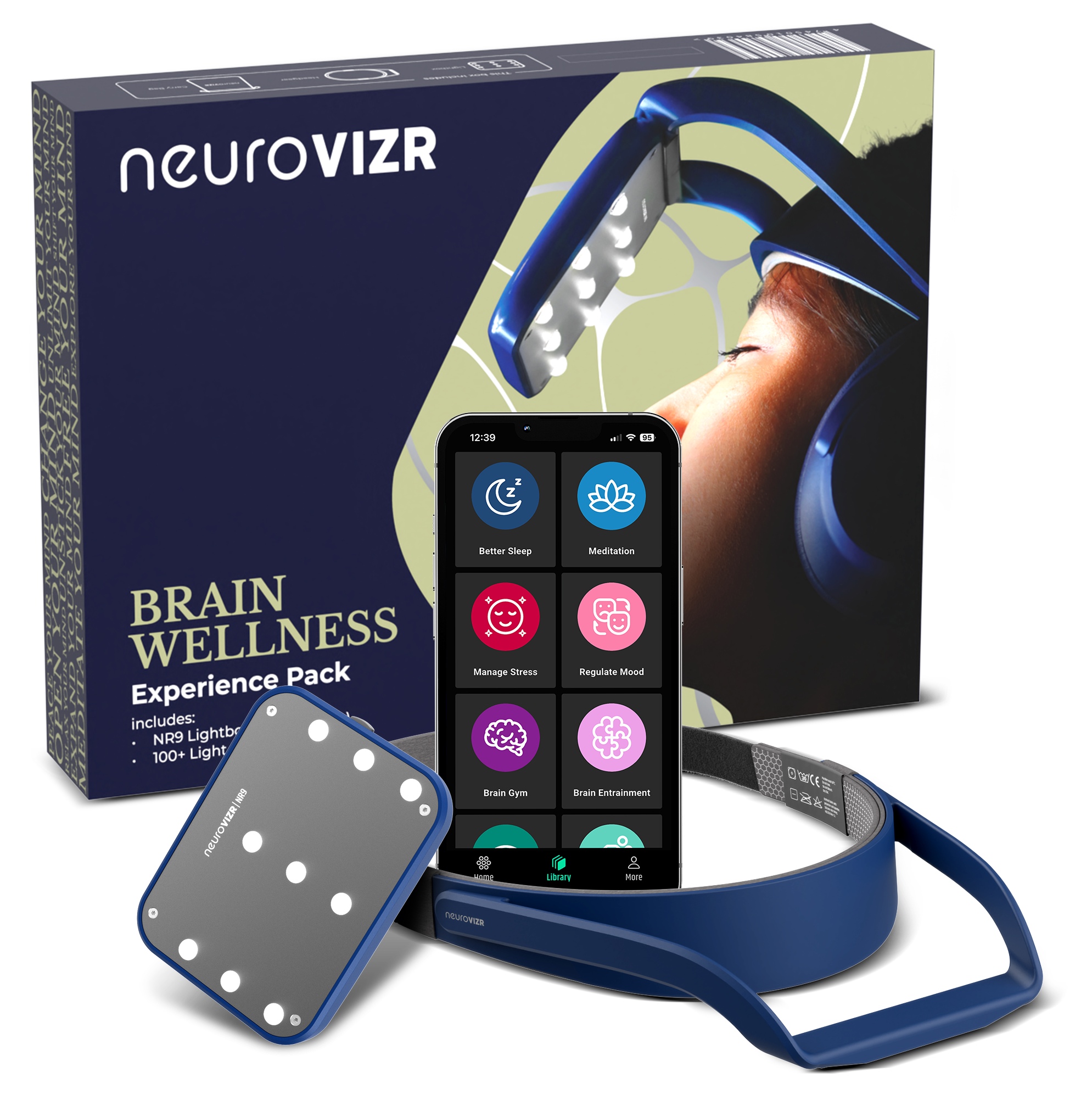
neuroVIZR Helps Produce Quality Sleep
Quality sleep begins with a regulated brain and a calm nervous system. This is where neuroVIZR plays a supportive role.
neuroVIZR is designed to guide the brain into balanced and relaxed states through targeted neural stimulation. By helping reduce mental overactivity and stress-related arousal, it supports the conditions needed for deeper, more restorative sleep.
When the brain shifts out of constant alert mode, sleep becomes more efficient. Transitions into deeper stages improve. REM cycles stabilize. Users often report falling asleep faster, staying asleep longer, and waking up feeling more refreshed. Rather than forcing sleep, neuroVIZR works by helping the brain return to its natural rhythm, allowing sleep quality to improve organically.
Final Thoughts
“Sleep is not a pause in life. It is where the brain quietly prepares you for it.”
Sleep is not downtime. It is an active biological process that restores the brain, regulates emotions, and protects long-term health. Each night, the brain carries out complex work that shapes how you think, feel, and respond the next day, often without you ever realizing it.
Understanding the science of sleep reminds us that better sleep is not about forcing routines or chasing perfect numbers. It is about creating the right conditions for the brain to settle into its natural rhythm. When the nervous system is calm and the brain is balanced, sleep becomes deeper and more efficient. This is where supportive brain wellness tools like NeuroVIZR can play a meaningful role by helping the brain shift out of constant alert mode and into true recovery.
When sleep quality improves, clarity returns, stress softens, and both mind and body begin to work in quiet harmony again.
FAQs
What is the Science of Sleep?
The science of sleep is the study of what happens in the brain and body while we sleep. It explains how sleep cycles work, how the brain processes memories and emotions at night, how the nervous system resets, and why sleep is essential for mental clarity, physical recovery, and emotional balance. Rather than being a passive state, sleep is an active biological process that supports brain health, immunity, learning, and stress regulation.
Is the Science of Sleep worth watching?
Yes, it can be worth watching depending on what you are looking for. If you enjoy content that explores the mind, dreams, and how the brain works beneath the surface, it can be engaging. It is not a clinical or instructional guide to improving sleep, but it offers insight into the emotional and psychological side of sleep and dreaming, which many people find thought-provoking.
What is the Science of Sleep called?
If you mean the movie, The Science of Sleep dives into dreams, imagination, and that fuzzy space where sleep and real life mix. But if you’re talking about the scientific field, people usually call it sleep science or sleep research. That covers neuroscience, psychology, and physiology.
What is the 3:2:1 rule for sleeping?
The 3:2:1 rule makes it easier to wind down at night and actually get good sleep. Here’s how it works:
Three hours before you hit the sack, put the brakes on heavy meals. Two hours out, shut down work and anything that makes your brain race. When you’re an hour away from bedtime, ditch the screens and bright lights.
Doing this really helps your body relax, lets your brain start producing melatonin, and sets you up for deeper, better sleep.





















Partager:
How Lack of Sleep Impacts Mental Health
How Many Hours of Sleep Are Enough for Good Health? A Neuroscience-Informed Answer