Addiction doesn’t just affect habits it changes the very wiring of the brain. But here's the good news: what’s wired can be rewired.
Neuroplasticity the brain’s ability to reorganise and form new neural connections offers a double-edged sword when it comes to addiction. It plays a role both in the development of compulsive behaviours and in the brain’s capacity to heal. Understanding this neurological flexibility gives us powerful tools for recovery.
What Is Neuroplasticity?
Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s remarkable capacity to change its structure and function in response to experiences, behaviours, emotions, and even thoughts.
This process happens through:
-
Synaptic plasticity: the strengthening or weakening of existing connections between neurons
-
Structural plasticity: the formation of new neurons and synapses
Throughout life, our brain is constantly adapting. This is how we learn new skills, overcome trauma and yes, also how addiction takes root.
The Role of Neuroplasticity in Addiction
1. Addiction as Maladaptive Learning
Addiction hijacks the brain’s reward system. Drugs and compulsive behaviours overstimulate dopamine circuits, reinforcing actions that deliver a short-term “high.”
This creates strong neural pathways that associate pleasure with substance use. Over time, these behaviours become automatic, bypassing rational thought.
Key takeaway: Addiction is not just a lack of willpower it’s a form of deeply entrenched learning, courtesy of neuroplasticity.
2. Brain Regions Involved
-
Prefrontal Cortex: Responsible for decision-making and impulse control. Chronic addiction weakens its function, reducing self-regulation.
-
Amygdala: Linked to emotional memory. It stores triggers associated with craving and stress.
-
Nucleus Accumbens: The brain’s pleasure centre repeated substance use floods it with dopamine, reinforcing the behaviour.
Over time, these changes become hardwired, making relapse more likely unless new neural routes are formed. neuroplasticity therapy can help in this.
Neuroplasticity in Addiction Recovery: The Brain Can Heal
Thankfully, neuroplasticity is a two-way street. Just as harmful behaviours become ingrained, healthy behaviours can rewire the brain towards resilience.
1. Reversing the Damage
Studies show that:
-
Abstinence can lead to partial restoration of dopamine receptors
-
Meditation, exercise, and therapy increase grey matter in areas responsible for control and empathy
-
Mindful practices alter connectivity in default mode and executive networks, reducing cravings
Recovery is possible not just psychologically but neurologically.
2. Harnessing Neuroplasticity for Healing
Key methods that support brain rewiring:
|
Tool or Practice |
Brain Impact |
|
Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) |
Reframes automatic thoughts, builds rational circuits |
|
Mindfulness & Meditation |
Activates prefrontal cortex, reduces amygdala reactivity |
|
Aerobic Exercise |
Increases neurogenesis in hippocampus |
|
Journaling & Gratitude |
Builds reflective awareness, rewires emotional circuits |
|
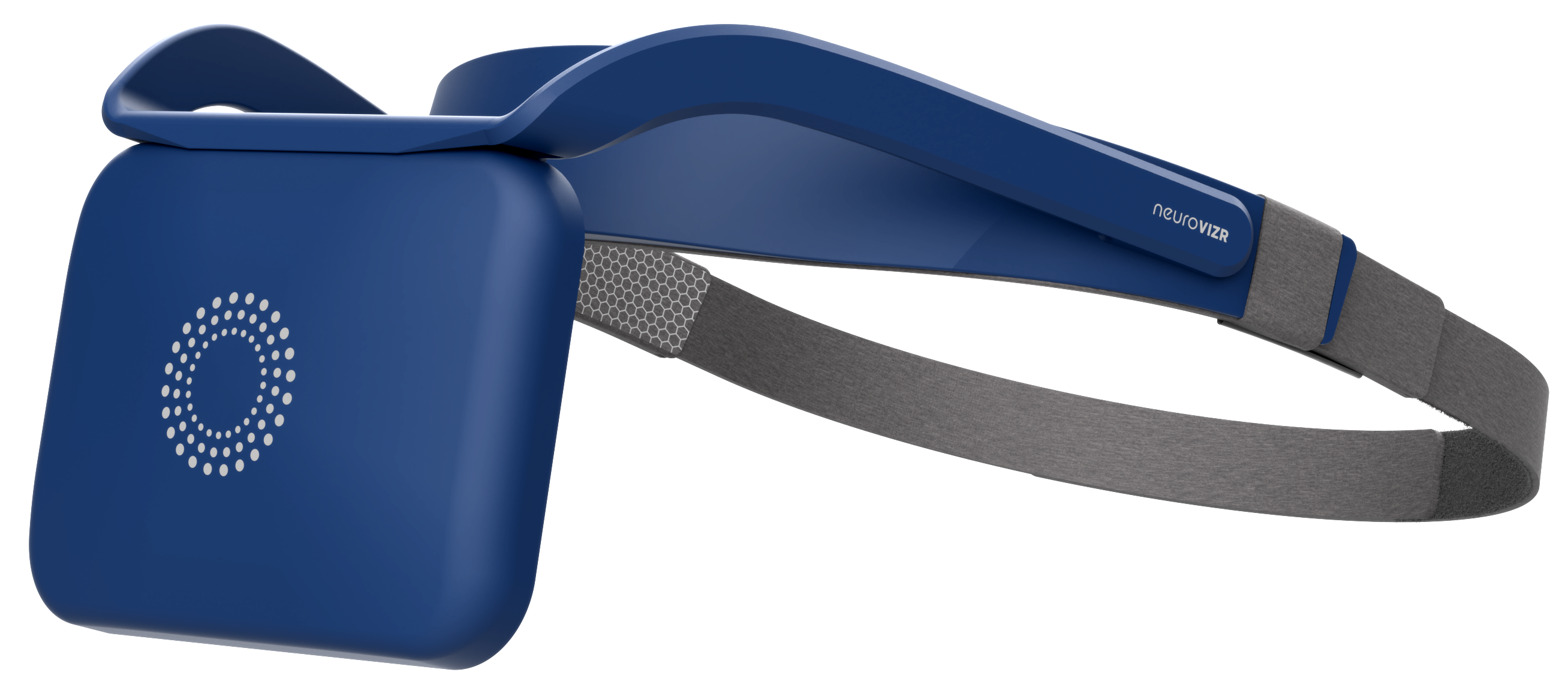
Neurotechnology (like neuroVIZR) |
Stimulates specific brainwave states for focus and calm |
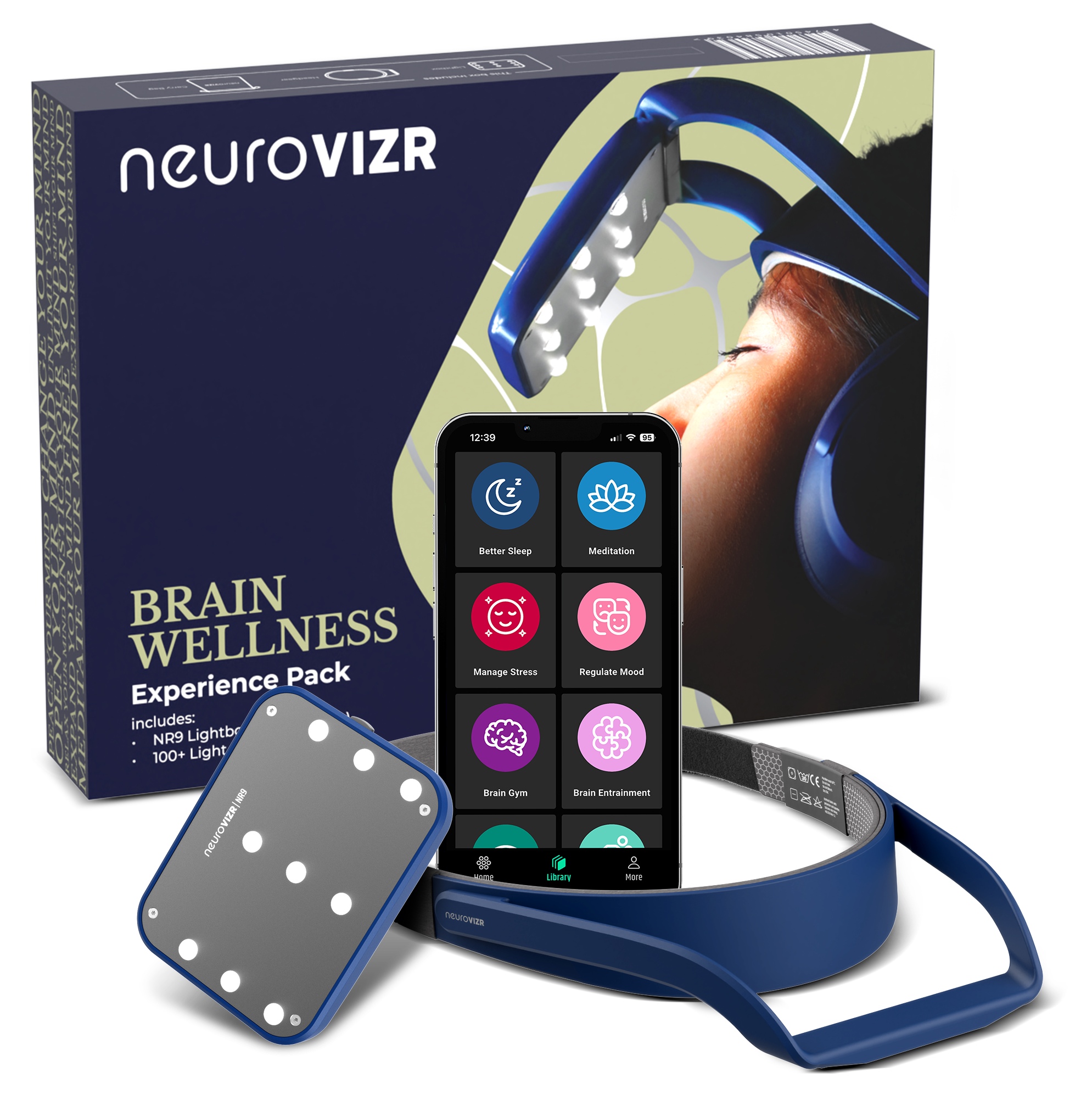
How neuroVIZR Supports Positive Neuroplasticity
neuroVIZR brain training devices is a wearable neurotechnology designed to enhance brain states linked to focus, relaxation, and creativity. Using light and sound stimulation, it engages the brain’s natural plasticity to:
-
Support calm, focused recovery routines
-
Reduce stress reactivity (which often leads to relapse)
-
Reinforce healthy neural patterns through multisensory entrainment
Whether you're in recovery or simply optimising mental wellness, neuroVIZR neurotechnology device helps create the fertile ground for new habits to take root.
Misconceptions About Neuroplasticity in Addiction
Myth 1: The brain is permanently damaged.
Recovery and reorganisation are always possible, even after years of use.
Myth 2: Neuroplasticity means change is easy.
It takes repeated, consistent effort to rewire deeply conditioned behaviours.
Myth 3: Only young brains are plastic.
While plasticity slows with age, it never stops. Adults of any age can reshape their brain.
Practical Tips to Reinforce Recovery with Neuroplasticity
-
Build micro-habits: Tiny positive routines repeated daily are more effective than drastic changes.
-
Avoid triggers: Cut off cues that reinforce old neural patterns.
-
Practice mindfulness: Sit with cravings without acting on them it rewires impulse circuits.
-
Use tech mindfully: Tools like neuroVIZR or guided breathwork apps can help entrain healthier rhythms.
-
Be patient: New connections take time. Progress isn’t linear but it’s happening.
Final Thoughts: The Brain’s Capacity for Change
Addiction rewires the brain but so can healing. With the right tools, support, and understanding of neuroplasticity, recovery is more than possible it’s a neurological process already built into you.
Whether through therapy, lifestyle shifts, or cutting-edge tools like neuroVIZR your brain is always learning. You have the power to choose what it learns next.
FAQs
Can neuroplasticity help with addiction?
Yes. Neuroplasticity allows the brain to rewire unhealthy habits formed during addiction and supports the development of healthier patterns in recovery.
What is the role of neuroplasticity in recovery?
It helps create new neural pathways that improve emotional regulation, decision-making, and resistance to relapse.
Is alcohol bad for neuroplasticity?
Chronic alcohol use impairs brain flexibility, but with abstinence and healthy practices, much of the damage can be reversed.
What is the main root cause of addiction?
Addiction stems from a mix of genetics, trauma, environment, and repeated activation of the brain’s reward system.
Disclaimer: neuroVIZR is a wellness device created to promote relaxation, focus, and overall brain wellness. It is not a medical device, does not provide diagnoses, and is not intended to treat, cure, or prevent any medical condition. The device is not suitable for individuals with epilepsy. Experiences and results may vary from person to person.





















Share:
Neuroplasticity Therapy: How to Retrain Your Brain and Heal Faster
Positive Neuroplasticity: How to Rewire Your Brain for a Happier, Healthier You