Our brains are more adaptable than we once thought. Thanks to the science of neuroplasticity, we now know that the brain can rewire itself in response to learning, injury, or experience. Neuroplasticity therapy harnesses this power helping people recover from brain injuries, anxiety, and even chronic stress.
But what exactly is neuroplasticity therapy, and how does it work?
In this blog, we'll break it down in simple terms what it is, how it helps, what exercises boost it, and what habits hurt it. Whether you're healing from a concussion, dealing with anxiety, or simply want to boost your brain health, this guide is for you.
What Is Neuroplasticity?
Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to change and adapt throughout life. When you learn a new skill, practice mindfulness, or recover from an injury, your brain is literally rewiring itself. Neurons form new connections, old pathways weaken or strengthen, and your brain updates how it functions.
That’s what makes therapy based on neuroplasticity so powerful it’s not just managing symptoms, it’s actually changing the brain.
What Is Neuroplasticity Therapy?
Neuroplasticity therapy is a targeted approach that uses exercises, therapies, and lifestyle changes to promote healthy brain rewiring. It’s used to support people recovering from:
-
Concussions and brain injuries
-
Stroke
-
PTSD and trauma
-
Anxiety and depression
-
Chronic stress
-
Cognitive decline
It combines physical movement, sensory stimulation, cognitive training, and sometimes neuromodulation tools all aimed at activating specific brain regions and encouraging positive plasticity.
 How Does Neuroplasticity Therapy Work?
How Does Neuroplasticity Therapy Work?
Therapy that supports neuroplasticity works by activating underused or damaged brain pathways and encouraging the brain to form stronger, healthier connections.
Some of the techniques used include:
Cognitive exercises (like memory, attention, or problem-solving tasks)
Physical movement (especially aerobic exercise and balance training)
Breathwork and mindfulness (to regulate the nervous system)
Audio-visual stimulation (like neurofeedback or light therapy)
Sensory integration (tactile, auditory, and visual input)
Over time, these tools help improve attention, emotional regulation, cognitive flexibility, and resilience.
What Conditions Can Neuroplasticity Therapy Help?
While it’s not a cure-all, neuroplasticity therapy has shown positive outcomes in people with:
-
Mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI)
-
Post-concussion syndrome
-
Anxiety and panic disorders
-
Chronic fatigue and brain fog
-
Stroke recovery
-
Learning disorders (like dyslexia or ADHD)
-
Long COVID-related cognitive issues
The key is personalized, consistent, and well-structured therapy ideally guided by a neuroplasticity-informed clinician or program.
What Exercises Are Best for Neuroplasticity?
Want to boost your brain’s plasticity at home? Here are a few exercises with strong evidence:
- Aerobic exercise (like brisk walking or cycling) increases blood flow and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)
-
Dual-task training (e.g., walking while solving mental puzzles) strengthens coordination and executive function
-
Mindfulness meditation enhances attention and emotional regulation
-
Learning a new skill like a language, instrument, or even juggling
- Neurofeedback or audiovisual entrainment can help modulate specific brainwaves (especially for anxiety or ADHD)
These aren’t just good habits they’re ways to train your brain to change itself.
What Kills Neuroplasticity?
Just as some habits help your brain grow, others can block plasticity:
- Chronic stress and high cortisol levels
- Lack of sleep
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Poor nutrition (especially diets high in sugar and low in omega-3s)
- Substance abuse
- Negative thought loops or avoidance behaviors
If you're investing in neuroplasticity therapy, it's just as important to remove these barriers as it is to add healthy habits.
Tips to Support Neuroplasticity Daily
Here’s how to make neuroplasticity part of your everyday life:
-
Sleep 7–9 hours a night most brain rewiring happens during sleep
-
Practice mindfulness or gratitude daily
-
Get 30 minutes of physical activity
-
Challenge your brain with something new weekly
-
Reduce screen time and multitasking
-
Eat brain-friendly foods (like salmon, berries, and leafy greens)
-
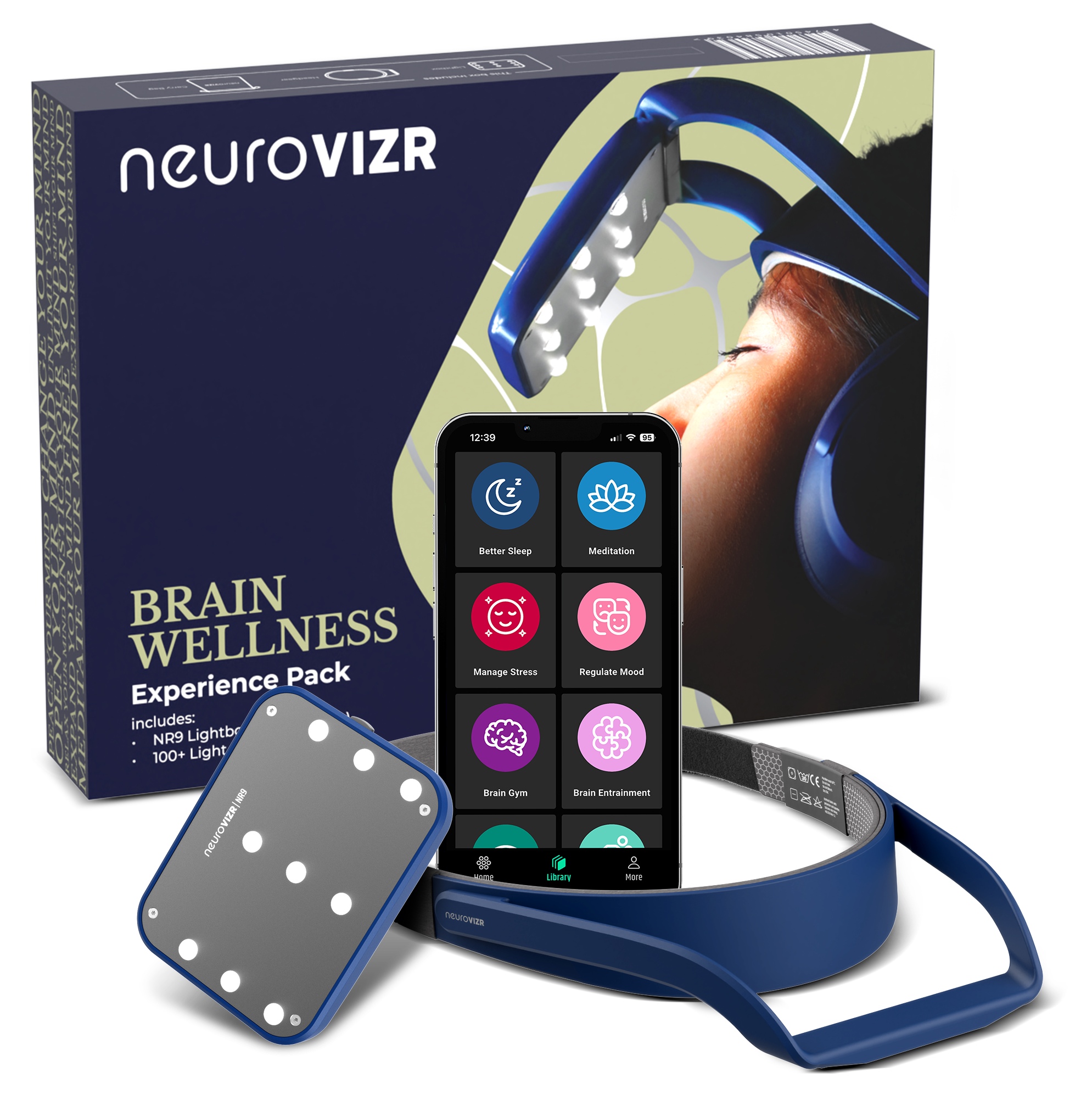
Use tools like neuroVIZR to support brain state flexibility
Your brain responds to what you do often make those inputs healthy.
Final Thoughts
Neuroplasticity therapy offers real hope not just to cope, but to change. Whether you're recovering from a concussion, living with anxiety, or just want to perform at your cognitive best, rewiring your brain is possible.
With the right tools, consistent practice, and expert support, you can shape how your brain works for the better.
Want to explore tools that support neuroplasticity at home? Learn more about how neuroVIZR can help support your mental wellness, clarity, and cognitive agility.
FAQs
What exercise is best for neuroplasticity?
Aerobic exercise (like walking, swimming, or cycling) is one of the most effective. It increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which promotes the growth of new neurons and connections.
What are the 4 types of neuroplasticity?
The four primary types are:
-
Structural plasticity (physical changes in brain structure)
-
Functional plasticity (shifting functions between areas)
-
Synaptic plasticity (strengthening or weakening of synapses)
-
Neurogenesis (the growth of new neurons, especially in the hippocampus)
How can you improve neuroplasticity?
Regular movement, good sleep, a healthy diet, stress reduction, and continuous learning all improve your brain’s ability to rewire itself.
What kills neuroplasticity?
Chronic stress, poor sleep, inactivity, poor diet, and mental stagnation can block the brain’s ability to adapt and grow.
Disclaimer: neuroVIZR is a wellness device designed to support relaxation, focus, and overall brain wellness. It is not a medical device and does not diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any medical condition. Results may vary from person to person.




















Share:
Neuroplasticity and Anxiety: How to Rewire Your Anxious Brain?
Neuroplasticity and Addiction: How the Brain Rewires and Recovers