Mental toughness is often talked about in sports as if it is a personality trait Some young athletes seem confident and composed while others struggle with pressure nerves or sudden loss of focus But mental toughness is not fixed It is a trainable brain skill shaped by development daily stress levels and the environments young athletes move through Many young athletes are not struggling with motivation They are navigating a nervous system that is still learning how to stay stable under intensity
Young Athletes Struggle Under Pressure
Young athletes are often expected to stay composed even when the situation feels bigger than their current capacity The truth is that the developing brain handles stress very differently from an adult brain The prefrontal cortex responsible for decision making emotional regulation and focus is still maturing During stress the amygdala becomes more active pulling the young athlete into worry hesitation or overwhelm This is why a usually skilled athlete may freeze before a serve forget a routine or feel sudden self doubt before a key moment
Mental toughness begins with recognizing that this reaction is not failure It is biology The brain responds to perceived threat before the athlete has a chance to think Athletes gain real confidence when they learn how to steady this system instead of fighting it.
Read more - mental training in sports
What Mental Toughness Actually Looks Like in the Brain
When an athlete is calm and focused the brain is in a state of flexible attention The prefrontal cortex guides choices movement timing and awareness But when the nervous system senses threat adrenaline rises breathing becomes shallow and the body shifts into survival mode This pulls the athlete away from strategy and into instinct
Mental toughness is the ability to stay in that flexible zone even when the environment becomes intense It is not about being emotionless It is about keeping the brain available for clear decisions Movement feels smoother Timing improves Confidence becomes stable
This capacity grows through repetition nervous system regulation and brain based training
Practical Tools That Build Mental Toughness in Young Athletes
Athletes do not build resilience by pushing through stress They build it by training the brain to return to calm quickly and reliably Here are simple tools that support that development
Breath Reset Before Performance
Slow steady breathing helps shift the nervous system out of overactivation A simple practice of inhaling through the nose and extending the exhale signals safety to the brain This can be done on the sideline in the locker room or even moments before starting a routine
Grounding for Stability
Placing awareness back into the body helps redirect the mind away from spiraling thoughts Feeling the feet on the ground noticing the sensation of holding equipment or focusing on posture helps re anchor the brain into the present moment
Mental Rehearsal for Confidence
Rehearsing movements or sequences quietly in the mind activates the same neural pathways used in real performance This builds familiarity and reduces the intensity of pressure once the athlete steps into actual competition
Micro Recovery Throughout Training
Short structured pauses during practice help the developing brain process skillwork and prevent overload These small recovery windows build greater endurance for focus and resilience. You must read about the sport psychology activities for athletes.
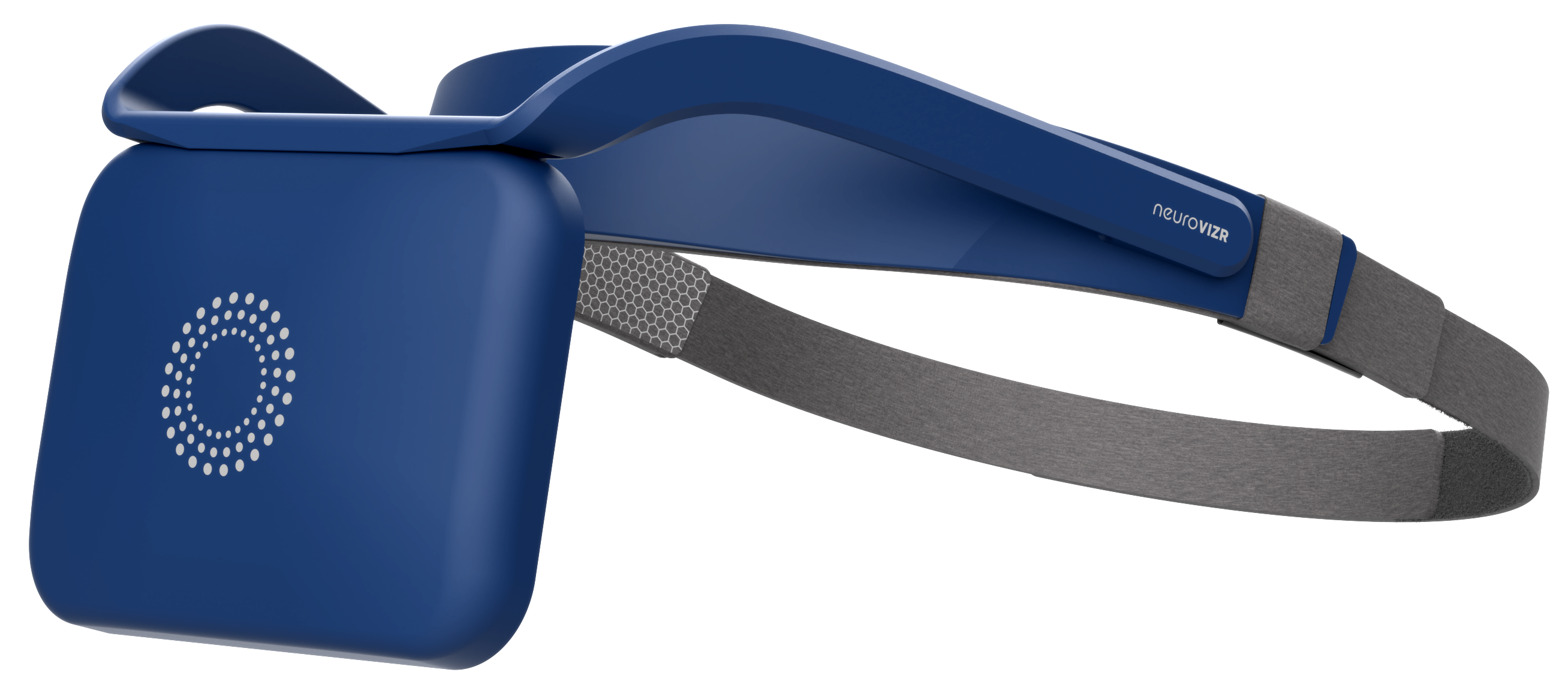
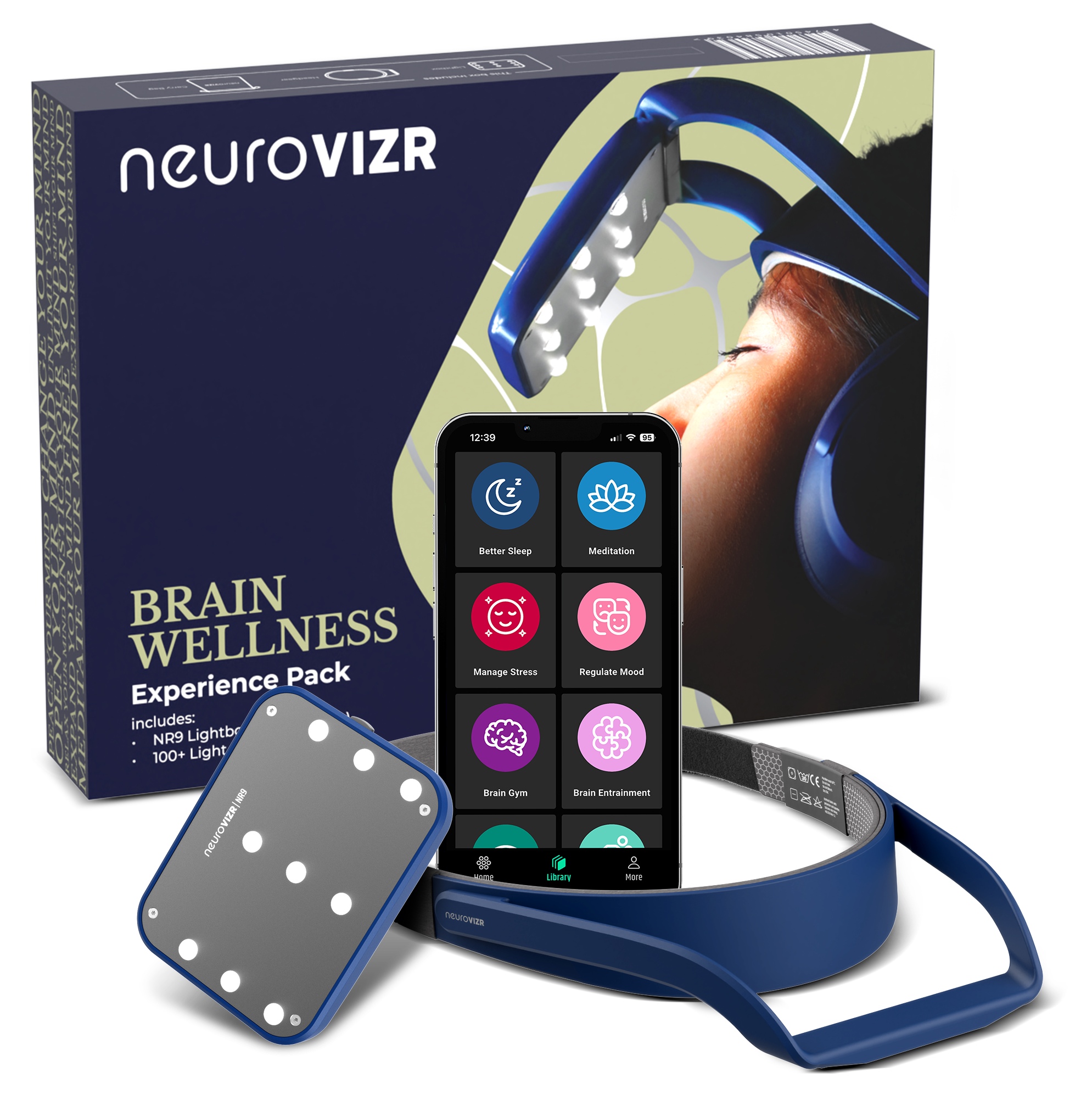
How Neurotechnology Supports Young Athletes
neuroVIZR does not promise performance changes instead it offers a structured light based experience that helps athletes pause reset and reconnect with their inner balance In the middle of school training social pressure and constant schedules young athletes often struggle to settle their mind neuroVIZR simply creates a guided sensory environment where focus and calm feel easier to access without forcing anything
Over time the familiar rhythm of the sessions can become part of a personal routine some athletes use it before training to centre themselves and others use it afterward to unwind It is a private self paced tool that fits naturally into their day giving them a moment to breathe slow down and come back to themselves This gentle consistency supports a steadier mindset which can make navigating challenges feel more manageable without making any performance or therapeutic claims
Conclusion-
Mental toughness for young athletes grows from consistent brain based training rather than sheer willpower. When they learn simple skills to regulate pressure, stay present and recover from mistakes their nervous system becomes more stable and responsive during competition. This foundation helps them make clearer decisions, maintain confidence and manage emotional spikes that often derail performance. Supportive tools and practices including structured mental skills training for athletes can strengthen focus, emotional balance and cognitive resilience in a practical and sustainable way. Over time young athletes build a mindset that is both strong and flexible allowing them to perform with steadiness while staying grounded and motivated on and off the field.
FAQs
What exactly is mental toughness for young athletes
Mental toughness is the ability to stay focused, steady and resilient under pressure. It is a trainable brain skill shaped by habits like breathwork, self talk and goal setting.
Can a young athlete really train their brain like a muscle
Yes, the brain strengthens through repetition similar to physical training. Practices such as visualization, emotional regulation and structured mental routines create more stable neural pathways.
How long does it take to build mental toughness
Most athletes begin noticing improvements within a few weeks of consistent mental skills training. Long term resilience develops through ongoing practice and supportive coaching environments.
What is the simplest way to help a child handle performance pressure
Start with small routines like slow breathing grounding and short pre performance cues. These calm the nervous system and reduce the intensity of stress signals in the brain.
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and does not provide medical advice diagnosis or treatment neuroVIZR is a wellness device and is not intended to treat cure or prevent any medical or psychological condition Always consult a qualified healthcare professional for concerns about mental health performance pressure or any condition affecting you or your child





















Share:
Mental Skills Training for Athletes
Sport Psychology Activities for Athletes